To assess physiological stress during physical work, the IAD laboratory and field studies use the measurement of physical forces.
The following classification is made:
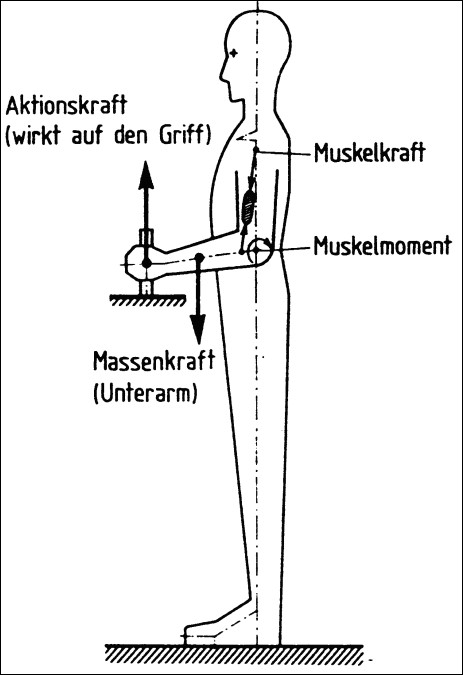
Whole-body force in the sense of DIN 33411 Part 1 is the force generated in connection with the human body. Whole body forces can be divided into muscle, mass and action forces:
- Muscle force is a physical force that acts through the activity of the muscles within the body. Muscle strength varies over a very wide range. Age, gender, physique, training and health are decisive influencing factors.
- Mass force is a body force that acts on the body mass as an inertial force, e.g. dynamically as an acceleration force for mobile workplaces or statically as a dead weight force.
- Action force is a physical force that acts outwards from the body. It results from the mass force, from the muscle force or from both together. In some specific cases, such a generalization does not apply. Mass force and muscle force can increase or decrease their effect depending on their amount and direction. The action force is used to perform a work activity. Since body stability plays an essential role in the assessment of strength, persons of greater weight can apply higher action forces at certain directions of force.
According to DIN 33411 Part 1, they are classified as driving, braking, manipulating or actuating forces.
Finger-hand forces are exerted by finger and hand muscles. There are both forces in force closure (without force effect to the outside) such as gripping forces, as well as vertical pressure forces with the thumb, the ball of the hand or the index finger, which act as action forces.